Warfarin Drug Interactions: What You Need to Know to Stay Safe
When you take warfarin, a blood thinner used to prevent dangerous clots in people with atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or artificial heart valves. Also known as Coumadin, it’s one of the most commonly prescribed anticoagulants—but also one of the most sensitive to what else you take. A single change in your routine—a new painkiller, a herbal supplement, even a big salad—can throw your blood’s clotting balance off track. That’s why warfarin drug interactions aren’t just a footnote in the prescribing info—they’re life-or-death details you need to know.
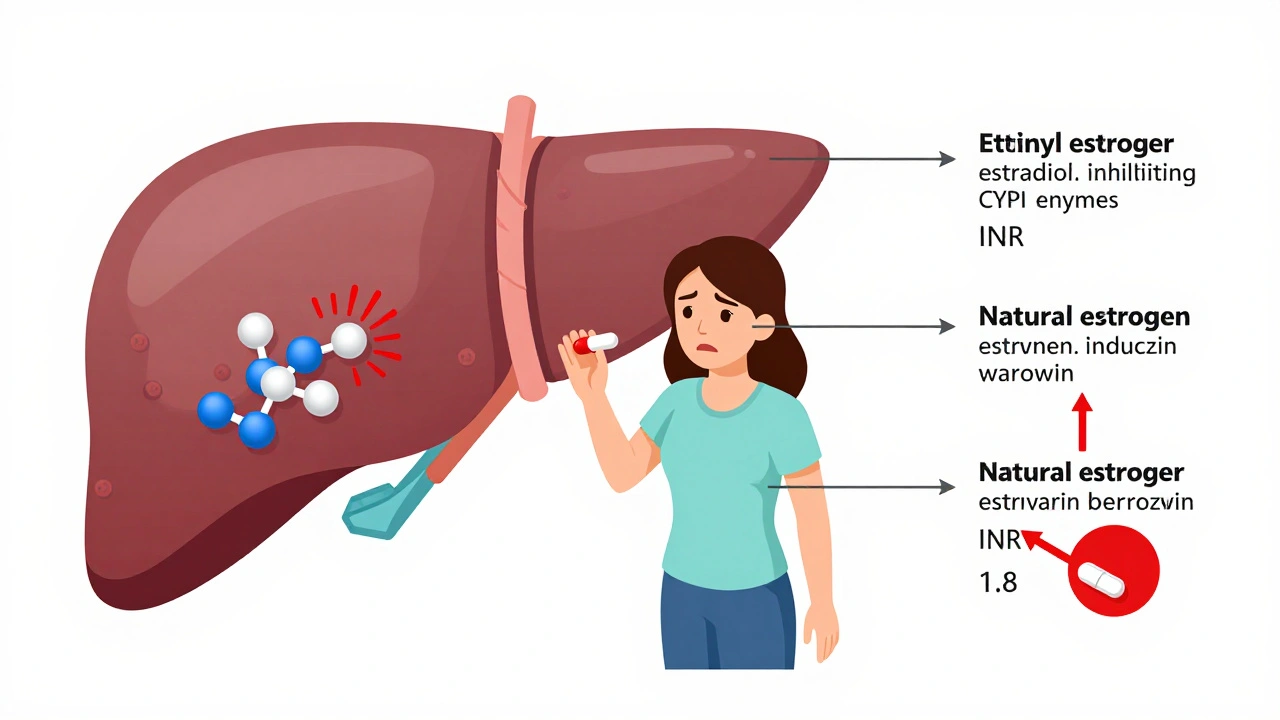
Warfarin works by blocking vitamin K, which your body needs to make clotting factors. Anything that changes how much vitamin K you absorb, or how your liver breaks down warfarin, can cause problems. Common culprits? antibiotics, like amoxicillin or ciprofloxacin, which can increase warfarin’s effect and raise bleeding risk. NSAIDs, including ibuprofen and naproxen, irritate your stomach lining and make bleeding more likely. Even vitamin K-rich foods, like kale, spinach, and broccoli, can lower warfarin’s effect if you suddenly eat more or less than usual. And don’t forget supplements: garlic, ginkgo, and St. John’s wort can all interfere. Your INR test—the blood test that measures how long it takes your blood to clot—is your only real safety net. If your INR goes too high, you risk internal bleeding. Too low, and you could get a stroke or clot.
That’s why the posts here focus on what really matters: knowing the difference between side effects and dangerous reactions, how to prepare for a medication review, and how to spot when something’s off before it becomes an emergency. You’ll find practical advice on managing multiple meds, understanding drug safety alerts like black box warnings, and avoiding hidden interactions that even your pharmacist might miss. This isn’t theoretical—it’s the kind of info that keeps people out of the ER. If you’re on warfarin, or care for someone who is, you’re not just following a prescription. You’re managing a delicate balance. The right knowledge doesn’t just help—it saves lives.
Estrogen can raise or lower your INR when you're on warfarin, increasing bleeding or clotting risk. Learn how birth control, HRT, and your genes affect warfarin dosing and what steps to take to stay safe.