QT Prolongation: Risks, Medications, and What You Need to Know
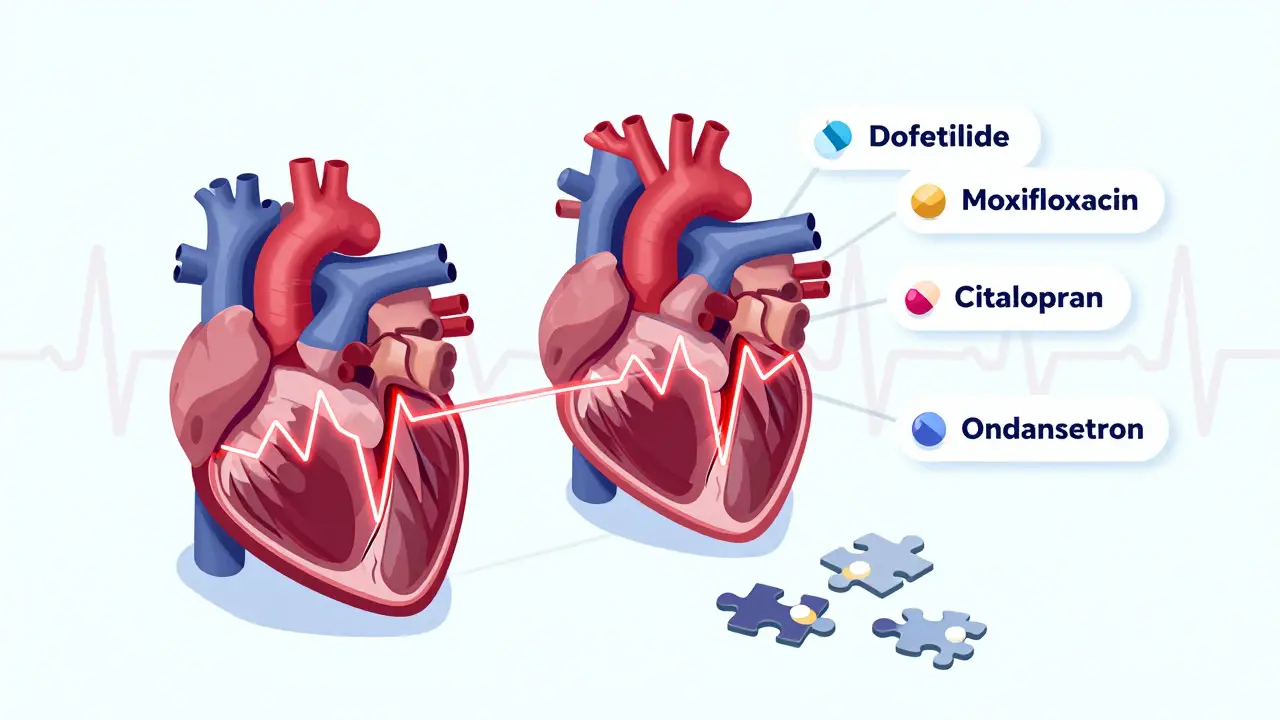
When your heart’s electrical rhythm gets out of sync, it can lead to something called QT prolongation, a delay in the heart’s electrical recovery phase that can trigger dangerous irregular heartbeats. Also known as long QT syndrome, it’s not always genetic—often, it’s caused by everyday medications. This isn’t just a lab result; it’s a real risk that can lead to torsades de pointes, a life-threatening type of irregular heartbeat that can cause fainting, seizures, or sudden cardiac arrest if left unchecked.
Many common drugs—antibiotics like moxifloxacin, antipsychotics, antidepressants, and even some heart meds—can stretch out the QT interval. You won’t feel it happening. No chest pain. No warning buzz. That’s why doctors check your ECG before starting certain treatments, especially if you’re on multiple meds or have a history of heart issues. It’s not about avoiding medicine—it’s about knowing which ones could quietly mess with your heart’s timing. Even over-the-counter antihistamines and herbal supplements like Nirdosh can interact in ways that raise the risk, especially when mixed with other drugs.
People with low potassium or magnesium, older adults, women, and those with kidney or liver problems are more vulnerable. But it’s not just about your health history—it’s about what’s in your medicine cabinet right now. A simple change in dosage or adding a new pill can tip the balance. That’s why understanding medication side effects, how drugs interact and what hidden risks they carry matters more than ever. You don’t need to fear your prescriptions, but you do need to ask the right questions: Could this affect my heart? Am I on something that’s known to cause QT prolongation? Is there a safer alternative?
The posts below dig into exactly this—real cases, real drugs, and real risks. You’ll find clear comparisons of antibiotics like Zyvox and moxifloxacin, how ADHD meds and antidepressants like Prozac and Paxil can play a role, and what alternatives exist when safety is the priority. No fluff. No jargon. Just what you need to spot the warning signs and talk to your doctor with confidence.
QT prolongation from medications can lead to sudden cardiac death. Learn the top risk factors-including drug combinations, electrolyte imbalances, and heart conditions-that make this deadly interaction more likely-and how to prevent it.
Over 400 medications can trigger dangerous heart rhythm problems. Learn the warning signs like palpitations and dizziness, which drugs are most likely to cause issues, and how to manage or prevent drug-induced arrhythmias before it's too late.